Pneumonia & Other Respiratory Infections
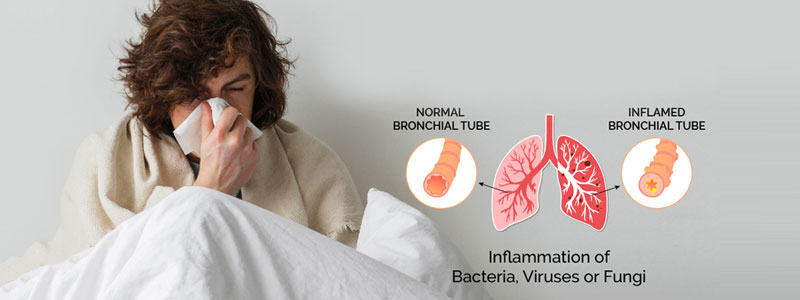
Pneumonia is a type of acute respiratory infection that causes inflammation of the air sacs (alveoli) in one or both lungs. The alveoli may fill with fluid or pus, leading to cough, fever, and difficulty breathing.
Causes of Pneumonia:
- Bacteria – e.g., Streptococcus pneumoniae, Haemophilus influenzae
- Viruses – e.g., influenza, RSV, SARS-CoV-2 (COVID-19)
- Fungi – more common in immunocompromised individuals (e.g., Pneumocystis jirovecii, Aspergillus)
- Aspiration pneumonia – inhalation of food, vomit, or liquids into the lungs
Symptoms of Pneumonia:
- Fever, chills
- Productive or dry cough
- Chest pain (especially on breathing or coughing)
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Rapid breathing or heartbeat
- Confusion, especially in elderly patients
Prevention:
- Vaccination
- Good hygiene – handwashing, covering mouth when coughing
- Avoid smoking – impairs lung defense
- Proper nutrition and care in children and the elderly
Other Common Respiratory Infections
- Bronchitis: Usually self-limiting and resolves without antibiotics
- Bronchiolitis: Can be serious in children under 2 years of age
- Influenza (Flu): Can lead to secondary pneumonia, especially in the elderly or immunocompromised
- COVID-19: Can cause viral pneumonia and severe respiratory complications
- Tuberculosis (TB): Requires long-term treatment with multiple antibiotics
